Task 18 deals with PV off-grid systems. The objective of the Task is to identify innovations which drive the PV off-grid technology and impact the market. That applies to the whole supply- and value chain including planning, financing, design, construction, operations, and maintenance of off-grid and edge-of-grid systems. The most important areas of innovation are addressed, including the technology change coming from lithium-ion battery systems, LED lighting, price reduction of solar modules and the whole area of digitalisation. All those aspects significantly change the structure of PV off-grid systems and allow for the installation of such systems as well as edge-of-grid systems close to existing grids and interconnected systems.
This Task focuses especially on challenges that are common across nations, markets, and system scales. It aims to provide solutions, tools, guidelines, and technical reports for free dissemination to those who might benefit from them.
Within the context of off-grid and edge-of-grid photovoltaic systems, the central discussion points include:
Task 18 has also worked on lithium-ion battery systems within PV off-grid applications and looked into best practice case studies, showed the advantage of this technology and re-simulated existing systems in order to underline the performance of this technology.


System simulations of data of existing systems in the field have been performed. The method was to create a digital twin from the data of a lithium-ion PV off-grid system. Within the simulation environment many parameters can be changed within a short period of time. Also the lithium-ion battery can be virtually replaced by a lead-acid battery.
With the help of sensitivity analyses, a recommendation can be given under which circumstances which battery chemistry shall be preferred.
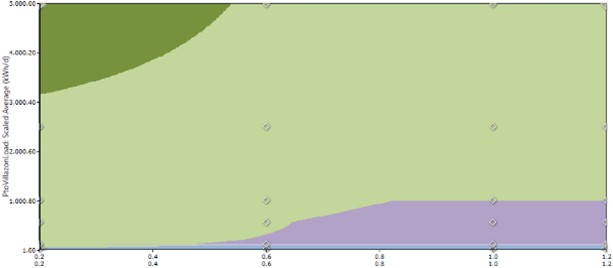
The outcome shows that lead-acid batteries (purple area) shall be preferred for small systems and for high prices of lithium-ion systems. Once a certain system size has been reached lithium-ion systems dominate.
A report has been processed and introduced to the publication process.
Energy Hubs – Compatibility and interconnection of Off-Grid systems as they grow.
The working group is preparing a report which showcases the powerful combination of electricity and heat supply for an island in the Netherlands that is connected to the mainland via a low power line. It shows how a high renewable fraction can be implemented in edge-of-grid areas with the help of energy hubs.
Digitalization in Off-Grid PV Systems
A systematic research on digitalisation and ICT in off-grid PV systems based on scientific publications and technical reports has been realised. During this research, a classification of digital technologies along the value chain of off-grid PV projects will be performed. Finally, the degree of innovation and progress of each technology will be undertaken to better understand trends and progress for each stage of the value chain.
Among all value chain categories described in figure 3 available digital tools have been collected and summarized.
The result was brought into a report which started the publication process. The content will also be visible at Energypedia.
Sustainable training schemes have been a part of the 2024 work. An inventory of existing training programs for maintenance in Tanzania was conducted, with a special focus on the target groups, their educational background, and their roles in the organization and implementation of maintenance. The distribution of roles varies significantly based on the system’s institutionalisation (ownership model and maintenance model), which can be completely private, state-organized, cooperative, non-commercial through a non-governmental organization (NGO), or in mixed forms.
In 2024 the Task 18 working group started a process to review and adapt the existing working plan. Finally, a new working plan was released and approved by Exco in November 2024. This new plan defines the work for Task 18 until April 2026.
The focus of work continues with the described work packages and shall result in the publication of 3 reports within 2025.
For 2025 the working group aims to meet at the Intersolar in Munich for the annual face to face meeting to coordinate the work.
Intertask activities are planned to connect to Task 17. The focus of this Task is significantly different from Task 18, but both activities target systems with lithium-ion batteries and operate independently from the main grid.
Regarding dissemination it is planned to present the published work at international conferences.
Task 18 will dedicate the majority of its efforts to larger and more complex off-grid and edge-of-grid system issues. IEA PVPS Task 11 addressed many of the issues arising at the time for smaller off-grid systems, however the industry has moved significantly since the closure of Task 11:
The objective of Task 18 is to find the technical issues and barriers which affect the planning, financing, design, construction and operations and maintenance of off-grid and edge-of-grid systems, especially those which are common across nations, markets and system scale, and offer solutions, tools, guidelines and technical reports for free dissemination for those who might find benefit from them.
The issues that will be focused on with regard to off-grid and edge-of-grid photovoltaic system will centre on:
This activity will broadly research and summarise the significant innovation and increased sophistication of off-grid and edge-of-grid systems over the past 8 years (since the closing of Task 11). A particular focus will be given to:
The goal of this subtask is to reach a maximum level of task work product dissemination, to cooperate with Industry Associations, Consultancies, Academia and other industry participants and to tailor the workings of Task 18 in order to limit any redundancy with other groups and/or increase the value of Task 18 work output for other groups. Key groups for collaboration are other IEA PVPS Tasks, the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) and Mission Innovation (a European Union initiative borne out of COP21)
This activity will distribute reports, models and tools through partner newsletters, workshops, webinars and presentations. The Task will also make use of social media group work platforms and communication platforms to achieve deliverables and foster engagement. The Task also has its own website which will be used as a repository for all meeting minutes, agendas, progress updates, etc. The IEA PVPS will, of course, be treated as the official repository of all finalised Task 18 work output